Describe the Brain-based Reason People Get Addicted to Drugs.
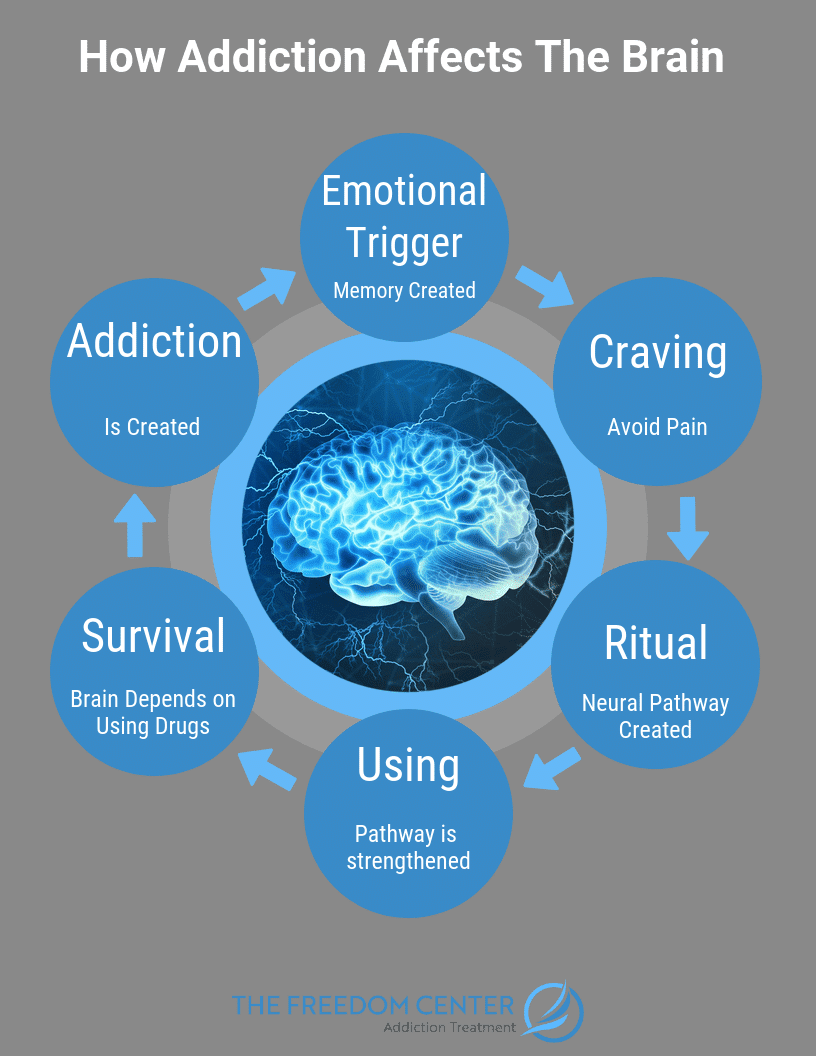
As described in our first post of this blog series alcohol and drug abuse trigger a rush of dopamine in the reward system of the brain. Physical addiction appears to occur when repeated use of a drug changes the way your brain feels pleasure.

The Science Of Addiction Heads Up
Drugs act on hedonic hot spots located in the mesolimbic dopamine system.

. Endorphins muffle your perception of pain and boost feelings of pleasure creating a temporary but powerful sense of well-being. Addiction has been described as a medical disorder that affects the brain and changes behavior 1 Various substances including alcohol illicit drugs prescription. The drugs become associated with the primal reward system in the brain.
The brain releases a controlled amount of dopamine when you experience natural pleasures. Drug addiction is a disorder in which the brain and the behavior of a person is affected which leads to an inability to control the use of a legal or an illegal drug or medication. When the animal gets hungry it seeks food.
And other things you enjoyed like food and hanging out with family may give you less pleasure. But theres more to what drugs do to the addicted brain than a simple dopamine surge. Addiction occurs when repeated use of drugs changes how a persons brain functions over time.
This causes the euphoric high that keeps drug users coming back for more. Opioids are highly addictive in large part because they activate powerful reward centers in your brain. Characterized by muscle stiffness and tremors Parkinsons is caused by the death of dopamine-producing neurons in a section of the midbrain.
With repeated drug use the. Over the decades researchers noticed that a remarkably. All drugs of abuse trigger a surge of dopamine a rush of wanting in the brain.
Trauma Traumatic events such as the loss of a loved one involvement in a violent act or major accident and much more are often the biggest reasons why people get addicted to drugs. Drug addiction can start with experimental use of a drug or alcohol. Your brains basil ganglia and one of its regions the nucleus accumbens basically binge on the.
This is extremely common as individuals who go through traumatic events such as these are in need of quick physical and emotional release. When the addict is triggered by his addiction he seeks drugs. Addictions Effect on the Cerebral Cortex Drug Seeking and Cravings.
The transition from voluntary to compulsive drug use reflects changes in the brains natural inhibition and reward centers that keep a person from exerting control over the impulse to use drugs even when there are negative consequencesthe defining characteristic of addiction. Thats more than 6 of the US. In the brain of smokers monoamine oxidase activity is reduced leading to less dopamine getting broken down which promotes increased craving for products containing nicotine.
Neurons use chemicals called neurotransmitters to communicate. Drugabusegov states that there are two ways this disruption of the brain can happen. Experiencing unhealthy stress sadness and other negative emotions Seeing familiar places and people you abused substances with.
By imitating the brains natural chemical messengers and by overstimulating the reward circuit of the brain. These reasons and sometimes more than one of these reasons can easily lead a person to begin using drugs and alcohol to cope. Drugs cause an unnatural dopamine surge.
Self-Medicating is one of the top reasons that people abuse drugs and alcohol. These regions regulate activity in the frontal cortical regions. Addictions Effect on the Brains Reward System.
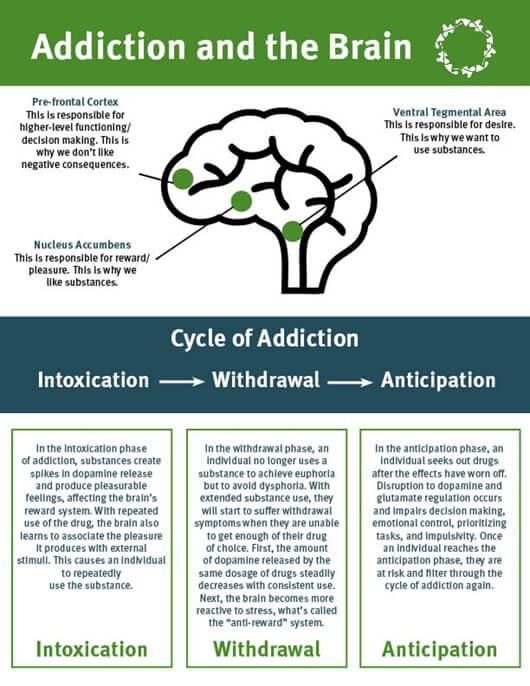
Addictive drugs and food particularly in obese individuals are believed to cause neurons from the ventral tegmental area to release the neurotransmitter dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. This pathway is referred to as the mesolimbic reward pathway arrows marked in red. Most drugs affect the brains reward circuit causing euphoria as well as flooding it with the chemical messenger dopamine.
Drugs have an effect on the way the brain communicates and they can affect the way nerve cells send receive and interpret information. There is no decision made. Drug addiction in the simplest terms is the strong compulsion to get and use substances even though a number of undesirable and dangerous consequences are likely to occur.
Substance-seeking behavior is often reinforced by emotional and memory triggers from the limbic system such as. The mesolimbic dopamine system is responsible for the feelings of pleasure that result from drug use. Self-medication can stem from stress anxiety undiagnosed mental illness severe depression loneliness and trauma.
1 Scientific research around the world continues to identify various risk factors such as genetics and environment which contribute to. The more drugs or alcohol youve taken the more disruptive it is to the brain Researchers have found that much of addictions power lies in its ability to hijack and even destroy key brain regions that are meant to help us survive. It is impossible for an addict to say to himself Stop WANTING to get high The basic animal rewards response is in play.
Opioids trigger the release of endorphins your brains feel-good neurotransmitters. These changes can remain long after you stop using the drug. When you use drugs for a long time it can cause changes in other brain chemical systems and.
The brain actually changes with addiction and it takes a good deal of work to get it back to its normal state. What happens in addiction is that through completely natural processes involved in all learning the brain prunes nerve pathways of attention and motivation to preferentially notice focus on. Addiction is a complex chronic disease that affects the brain and occurs due to many different underlying causes.
A properly functioning reward system motivates a person to repeat behaviors needed to thrive such as eating and spending time with loved ones. Experts estimate that more than 18 million people ages 12 and older have used prescription drugs for nonmedical reasons in the previous year. The mesolimbic dopamine system is the location where cognitive thoughts about drugs occur.
Gradually it becomes more. Although the degree of intoxication from nicotine is substantially less than that of heroin or crack cocaine it can be as physically as addictive as both substances. Addiction Changes Brain Structures and Their Functioning Impaired Decision-making Impulsivity and Compulsivity.
The addicting drug causes physical changes to some nerve cells neurons in your brain. When addicted a person continues to use the drug despite the harm caused due to it. Answers a and b.
This makes us crave more drugs. Answers a and b.

Drugs Brains And Behavior The Science Of Addiction Safespace
Comments
Post a Comment